ADA seating refers to accessible seating arrangements provided in various venues to accommodate individuals with disabilities. These seats are designed to ensure compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), offering equal access to events and facilities.
Accessible seating, often referred to as ADA seating, is a mandatory aspect of public venues like concert halls, stadiums, and theaters. These seats are strategically placed to offer clear views while being easily accessible to those with mobility challenges, sensory impairments, or other disabilities. The requirements for ADA seating vary based on the venue’s size and type, ensuring that a certain percentage of the total seating capacity is accessible.
At concerts and other live events, ADA seating is crucial for inclusivity, allowing individuals with disabilities to enjoy performances in comfort. These seats are not exclusively reserved for disabled patrons; companions or family members can also use them, provided they are accompanying a person requiring ADA seating. However, it’s essential to understand that not just anyone can purchase ADA tickets; they are intended for those who genuinely need them due to a disability.

Stadiums and larger venues have specific ADA seating requirements, ensuring that accessible seating is available at different locations and price points. This diversity in placement and pricing allows for a more inclusive experience. In case of accidental purchase of ADA tickets by someone not requiring them, it’s advisable to contact the venue or ticketing service for guidance, as these seats should remain available for those who need them.
Pregnant women may also find ADA seating beneficial, as these seats often provide additional comfort and easier access. Ticketmaster and other ticketing platforms have guidelines and processes in place for accessible seating requirements, ensuring a smooth booking experience for those needing ADA seating.
For a more detailed understanding of ADA seating and its various aspects, including requirements at different venues and how to purchase these tickets, we invite you to read the detailed article below.
ADA seating, a crucial element in public venues, ensures accessibility for individuals with disabilities. It’s not just about providing a space; it’s about creating an inclusive environment where everyone, regardless of their physical abilities, can enjoy events. These seats are designed with specific features like extra space for wheelchairs, easy access to entrances and exits, and sometimes, specialized audio-visual equipment for those with sensory impairments.
The concept of ADA seating has evolved significantly since the Americans with Disabilities Act was passed in 1990. Initially, the focus was on basic accessibility, but over time, the emphasis has shifted to ensuring equal enjoyment of facilities. This evolution reflects a broader societal shift towards greater inclusivity and understanding of the diverse needs of people with disabilities.
The ADA sets forth clear guidelines for public spaces, mandating that they provide adequate and accessible seating for individuals with disabilities. These regulations are not just recommendations; they are legal requirements that venues must adhere to, ensuring that accessibility is not an afterthought but a key consideration in design and layout.
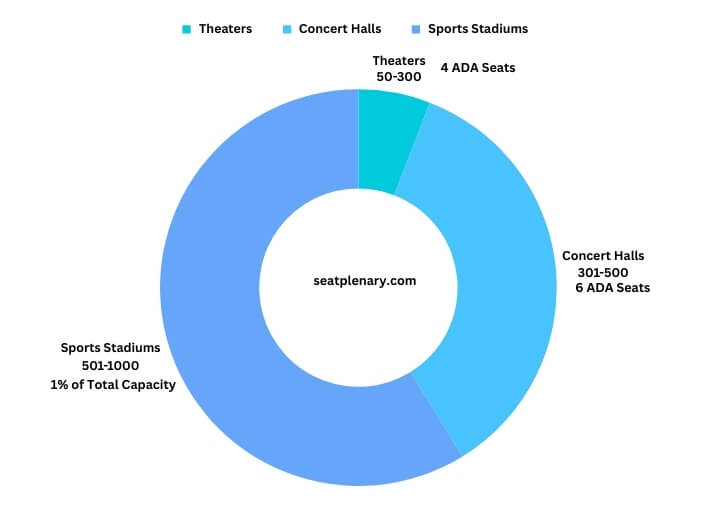
Each type of venue, from theaters to sports stadiums, has specific ADA seating requirements. These requirements are based on the venue’s capacity and layout, ensuring that a proportionate and appropriate number of seats are available for individuals with disabilities.
Compliance with ADA regulations is monitored by various government agencies. Venues found non-compliant may face legal action, including fines and mandatory modifications. This enforcement ensures that ADA seating is a priority for all public venues.
When designing ADA seating, several factors are considered. These include ease of access, proximity to restrooms and concessions, and unobstructed views. The goal is to ensure that these seats are not just compliant but also comfortable and functional for the users.
The placement of ADA seating varies depending on the venue’s layout. Ideally, these seats should be distributed throughout the venue, offering a variety of views and price options.
Purchasing ADA seats involves specific guidelines to ensure that these seats are reserved for those who genuinely need them. Venues and ticket sellers often require some form of verification or assurance that the purchaser or a member of their party qualifies for ADA seating.
Legally, ADA seats are intended for individuals with disabilities and their companions. This policy prevents misuse of ADA seating and ensures that they are available to those who truly need them.
Buying ADA tickets can be done both online and offline. Online platforms typically have a designated section for ADA seating, while offline purchases can be made through the venue’s box office, where staff can assist with specific requirements.
ADA seating is designed to cater to a wide range of disabilities, including mobility, visual, and auditory impairments. This inclusivity is vital for ensuring that all guests have equal access to enjoy events.
Interestingly, ADA seating is also available for those with temporary disabilities, such as injuries, and for pregnant women. This flexibility highlights the inclusive nature of ADA seating, catering to a broad spectrum of needs.
One of the biggest challenges for venues is balancing the need for ADA seating with space and design constraints. Additionally, ensuring that these seats provide an equivalent experience to standard seating can be complex.
To overcome these challenges, venues have adopted innovative solutions like adjustable seating and advanced booking systems. Sharing best practices and learning from successful implementations can help other venues improve their ADA seating.
Yes, ADA seating is available at all public venues, as mandated by the Americans with Disabilities Act. This includes theaters, concert halls, sports stadiums, and any other place where the public gathers for events. The act requires these venues to provide accessible seating options that cater to various disabilities, ensuring inclusivity and equal access for all attendees. The number and location of these seats vary depending on the venue’s size and layout, but the underlying principle is to ensure that individuals with disabilities can enjoy events just like anyone else.
Absolutely, ADA seats can and should be reserved in advance. Most venues offer the option to book these seats ahead of time, either online or through their box office. This advance reservation system ensures that individuals requiring ADA seating can secure their spots before the event. It’s always a good idea to book these seats as early as possible, especially for popular events, as the number of ADA seats is limited and they can fill up quickly.
ADA seating ensures accessibility for wheelchair users by providing firm seats for wheelchairs in public venues. These designated spaces are strategically located to accommodate clear sightlines and easy access to amenities. By adhering to ADA guidelines, public venues can ensure that all patrons have equal opportunities to enjoy their facilities.
Venues can ensure accessibility for patrons seated behind the penalty box by providing clear sightlines and accommodating seating arrangements. By prioritizing the benefits of penalty box seats, such as unobstructed views and proximity to the action, venues can ensure all patrons have an enjoyable and inclusive experience.
Service animals are indeed allowed in ADA seating areas. The Americans with Disabilities Act recognizes the importance of service animals in assisting individuals with disabilities. Therefore, venues are required to accommodate service animals in ADA seating areas. These animals are trained to behave well in public settings, ensuring they do not disrupt the event while providing essential support to their owners.
If ADA seats are sold to non-disabled patrons, the venue is typically required to reaccommodate the individuals in appropriate seating if a person with a disability needs the ADA seat. Venues strive to ensure that ADA seating is reserved for those who genuinely need it. In cases where ADA seats are mistakenly sold to or occupied by non-disabled patrons, the venue staff usually works to resolve the situation amicably, often by relocating the non-disabled patrons to other seats.
Venues ensure ADA seating meets compliance standards by following the guidelines set forth in the Americans with Disabilities Act. These standards cover various aspects, including the number of ADA seats required, their location, and accessibility features. Venues often work with architects and compliance experts during the design and renovation stages to ensure all ADA requirements are met. Regular audits and inspections are also conducted to maintain compliance and address any issues promptly.
Yes, ADA seating is designed to accommodate different types of disabilities. This includes mobility impairments, where wheelchair-accessible spaces are provided, as well as accommodations for individuals with hearing and visual impairments. For instance, some venues offer special headphones for enhanced audio or provide spaces where guide dogs can comfortably sit. The goal is to cater to a wide range of needs, ensuring that all guests, regardless of their disability, can enjoy the event.
Venues that do not comply with ADA seating regulations can face significant penalties. These can include fines, legal action, and the requirement to make costly modifications to their facilities. Non-compliance not only has legal repercussions but can also negatively impact the venue’s reputation. Therefore, most venues take ADA compliance very seriously and strive to meet all the necessary requirements to ensure accessibility and inclusivity for all patrons.
ADA seating is more than just a legal requirement; it’s a commitment to inclusivity and equal access for all. From the historical evolution to the design and implementation challenges, ADA seating plays a pivotal role in making public venues welcoming and accessible to everyone.